 Overuse Injuries
Overuse Injuries
Overuse injuries do not result from a single traumatic event but rather from repeated stress to a specific area over time. Excessive, repetitive motion places significant strain on the feet, ankles, legs, knees, hips, and lower back. Athletes are particularly susceptible to these types of injuries due to the repetitive nature of their physical activities.
Common overuse injuries include:
Ankle Sprains
An ankle sprain involves a tear or disruption in a ligament, whereas a strain refers to inflammation or minor injury that does not result in a tear. Although ankle sprains are typically considered traumatic injuries, some individuals are biomechanically predisposed to them. If the foot is not aligned front to back, due to either an inversion or eversion deformity, this imbalance can increase the risk of sprains or strains.
Ligaments are strong bands of tissue connecting bones at joints. Sprains often occur when the foot rolls outward rather than inward, stressing the ankle's supporting ligaments. Ankle sprains are common in nearly all sports, whether contact or non-contact, and can range in severity. Recovery time may vary from five days to six weeks, depending on the extent of the injury.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries
ACL injuries occur when the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee is overstretched or torn. These injuries can occur during both contact and non-contact events, often resulting from a twisting force or hyperextension of the knee. Another mechanism involves the femur being forced across the tibia during a sudden stop or shift in weight.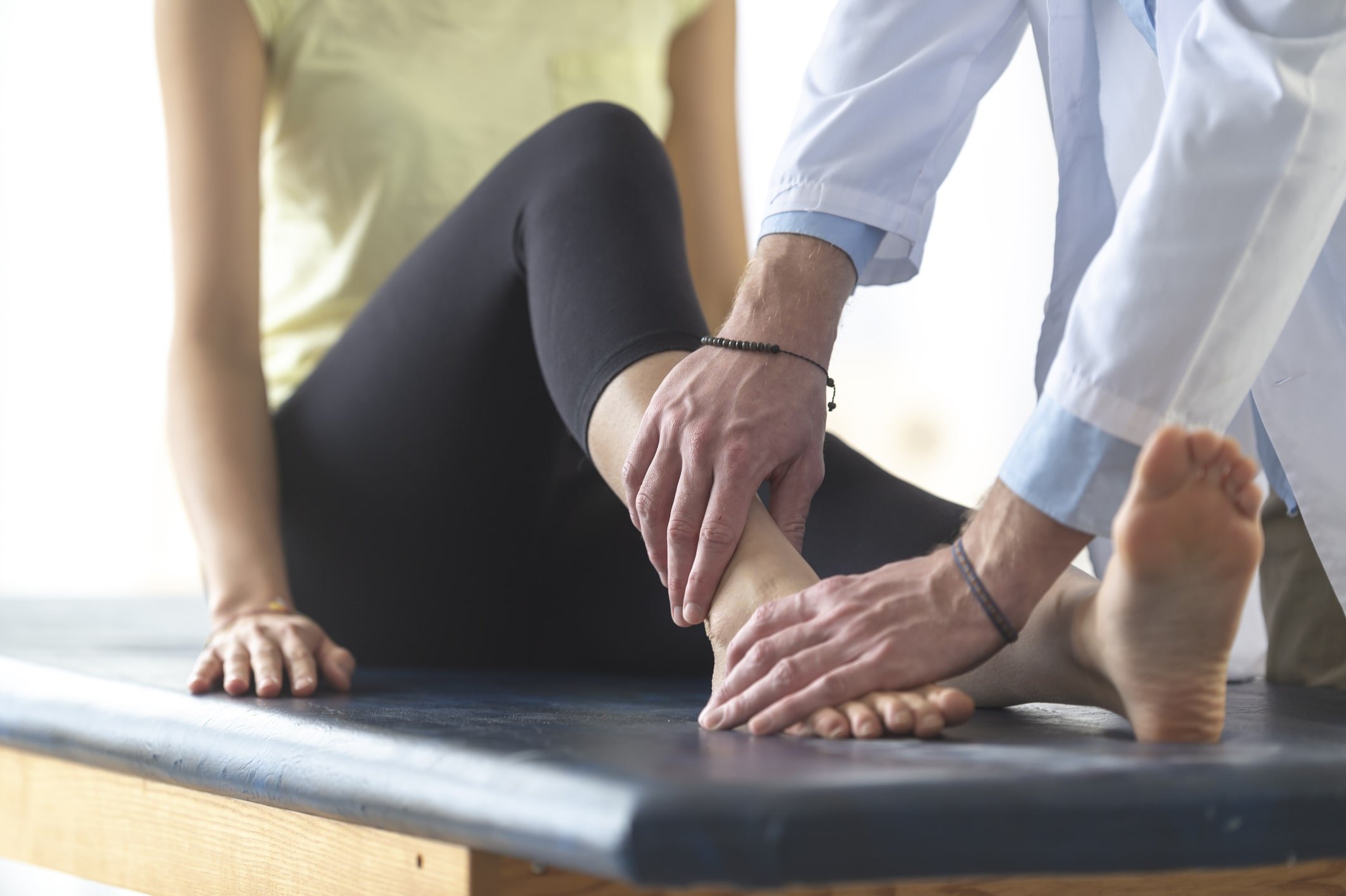 
Athletes with flat feet or pronated foot types are more prone to non-contact ACL injuries. Excessive or rapid pronation increases tension in the ACL—a condition known as preload tension—making it more vulnerable to tearing. Additionally, limb alignment, such as being "bow-legged" (genu varum), should be assessed, as it may increase the risk of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury. Corrective exercises and custom orthotics can help reduce abnormal loading on the ACL and prevent injury.
Achilles Tendinitis
The Achilles tendon is formed by the convergence of the deep and superficial calf muscles and attaches to the back of the heel. With age, the Achilles tendon receives less blood supply, making it more susceptible to inflammation, tears, and degeneration.
This condition is especially common in individuals with flat feet or high arches. In flat-footed individuals, the inward rolling of the leg causes a wringing effect, like twisting a wet towel, that impairs blood flow to the tendon. Achilles tendinitis can be acute or chronic and is often associated with overuse. Treatment includes physical therapy, muscle re-education, and correction of foot mechanics with custom orthotic devices
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (Runner’s Knee)
Patellofemoral pain, often referred to as anterior knee pain or runner's knee, affects both young and older athletes. It presents as a burning sensation between the kneecap and thigh bone and is typically caused by faulty biomechanics in the lower extremities, particularly at the foot and ankle. 
The patella sits within a V-shaped groove in the femur, gliding smoothly when the foot and heel are in neutral alignment. However, when the heel rolls inward, the patella may move out of this groove and grind against the cartilage, causing pain and dysfunction. Treatment includes gait analysis, custom orthotics to maintain proper alignment, and physical therapy to strengthen surrounding muscles. Without addressing foot alignment, physical therapy alone may not be sufficient to prevent recurrence.
X-rays taken in a weight-bearing position can be useful for assessing the mechanical structure, although they often appear normal. A negative X-ray is reassuring, indicating the issue is likely mechanical rather than structural.
Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS)
ITBS is a frequent source of hip and lateral knee pain in athletes. Rather than a friction issue, ITBS is better described as a compression syndrome, often caused by overpronation of the foot. This biomechanical dysfunction alters the hip's alignment and pulls the iliotibial band across the lateral femoral condyle, leading to irritation and pain.
The IT band runs from the hip to just below the knee, and symptoms can appear anywhere along its length. Mechanical instability contributes to ITBS, but symptoms can be alleviated through a combination of custom orthotics, supportive athletic shoes, and targeted physical therapy to stretch and strengthen the hip and knee musculature.
Shin Splints (Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome)
Shin splints refer to pain along the lower third of the tibia (shin bone), typically on the inner side. This condition arises when the muscles attached to the tibia are overworked due to excessive foot pronation or flattening, which is often the result of a forefoot-rearfoot misalignment.
As a result of this misalignment, the foot strikes the ground abnormally, forcing the leg muscles to overcompensate. This strain pulls on the muscle attachments along the tibia, potentially leading to a stress reaction or even a stress fracture if left untreated.
Pain may also occur on the outer part of the leg, near the knee, due to insufficient shock absorption and excessive pronation. Treatment involves a biomechanical examination, custom orthotics, appropriate footwear, physical therapy, and exercises that stretch and strengthen the lower extremities.
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis involves inflammation of the plantar fascia, the thick connective tissue running along the bottom of the foot. Heel pain—especially first thing in the morning—is the hallmark symptom. If left untreated, the condition can lead to fascia degeneration and the formation of painful heel spurs. 
The leading cause is excessive foot pronation, which overstretches the fascia and causes microtears. Treatment involves a comprehensive biomechanical evaluation, custom orthotic devices, and, if necessary, imaging such as weight-bearing X-rays or MRI to assess for a stress reaction or fracture.
Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain is often linked to abnormal foot mechanics, particularly overpronation. When the foot arch collapses excessively, it alters alignment from the ground up, causing the pelvis to tilt and compress the lumbar spine.
Many cases of non-traumatic low back pain stem from foot dysfunction. A biomechanical assessment and gait analysis can help determine if the pain originates from the feet. Treatment includes orthotic correction, targeted exercises (such as small squats, crunches, and bridges), and proper footwear to restore postural alignment and alleviate discomfort. Always assess foot posture before pursuing surgical or invasive interventions.
To schedule your comprehensive biomechanical evaluation, visit drleecohen.com or call our Sports Medicine Podiatry Center and book an appointment at our Marlton, N.J. Sports Medicine Facility or Ridley Park, P.A. Office location with one of our podiatric sports medicine specialists today by calling (610) 522-9200.

 -TRUSSTIC™ support system helps improve stability
-TRUSSTIC™ support system helps improve stability -Super lightweight
-Super lightweight - Lightweight design
- Lightweight design -Agility-speed-control outsole
-Agility-speed-control outsole Overuse Injuries
Overuse Injuries
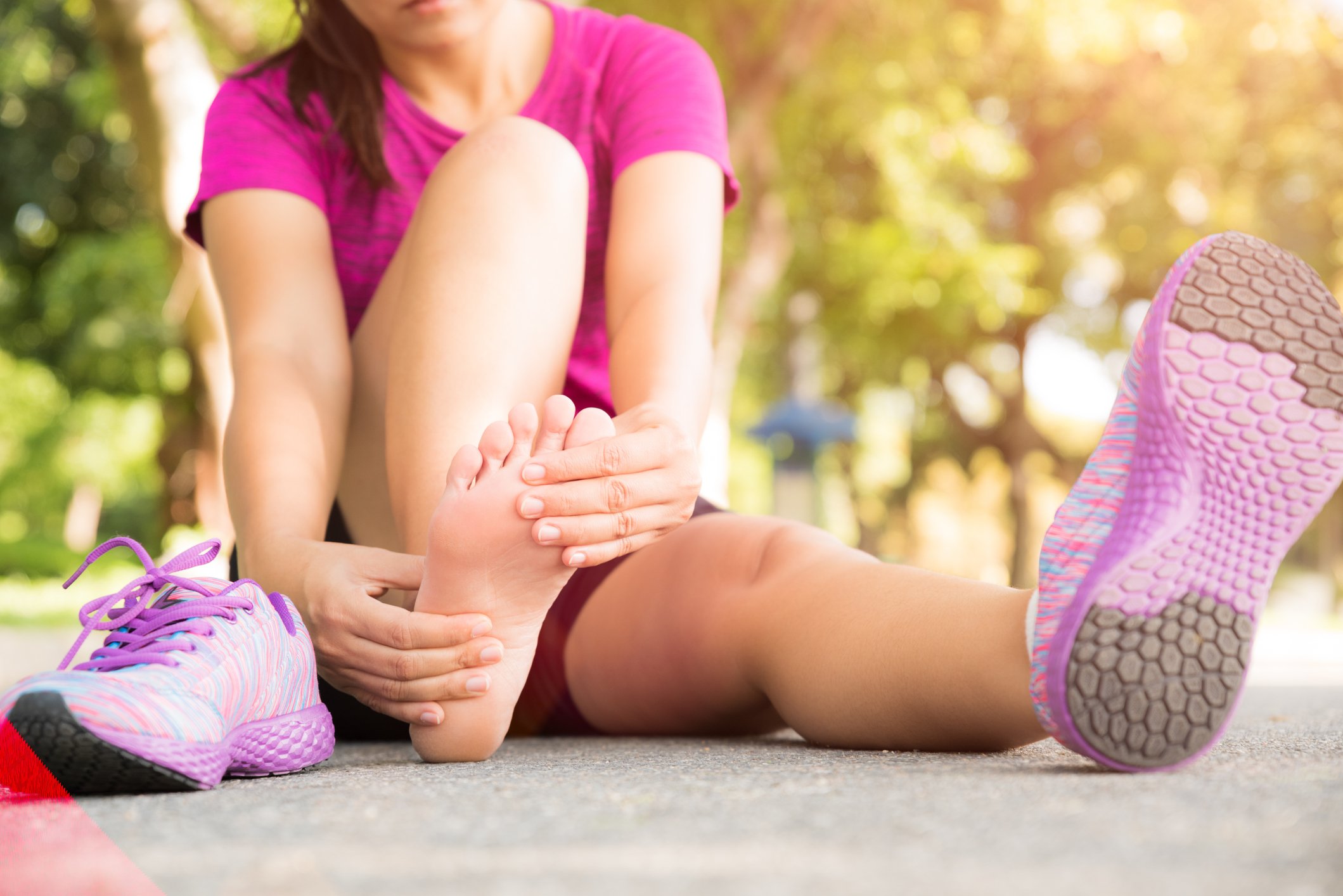

 According to the American Podiatric Medical Association, 75-77% of Americans have experienced foot pain at some point in their lives. It’s not surprising considering that each foot has 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments, that the average person walks around 7500 steps per day, and when running up to 4 times your body weight can be the pressure amount placed on your feet. Put all of that together and it’s no wonder that feet are prone to injury and are at high risk for developing a wide variety of painful conditions.
According to the American Podiatric Medical Association, 75-77% of Americans have experienced foot pain at some point in their lives. It’s not surprising considering that each foot has 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments, that the average person walks around 7500 steps per day, and when running up to 4 times your body weight can be the pressure amount placed on your feet. Put all of that together and it’s no wonder that feet are prone to injury and are at high risk for developing a wide variety of painful conditions.
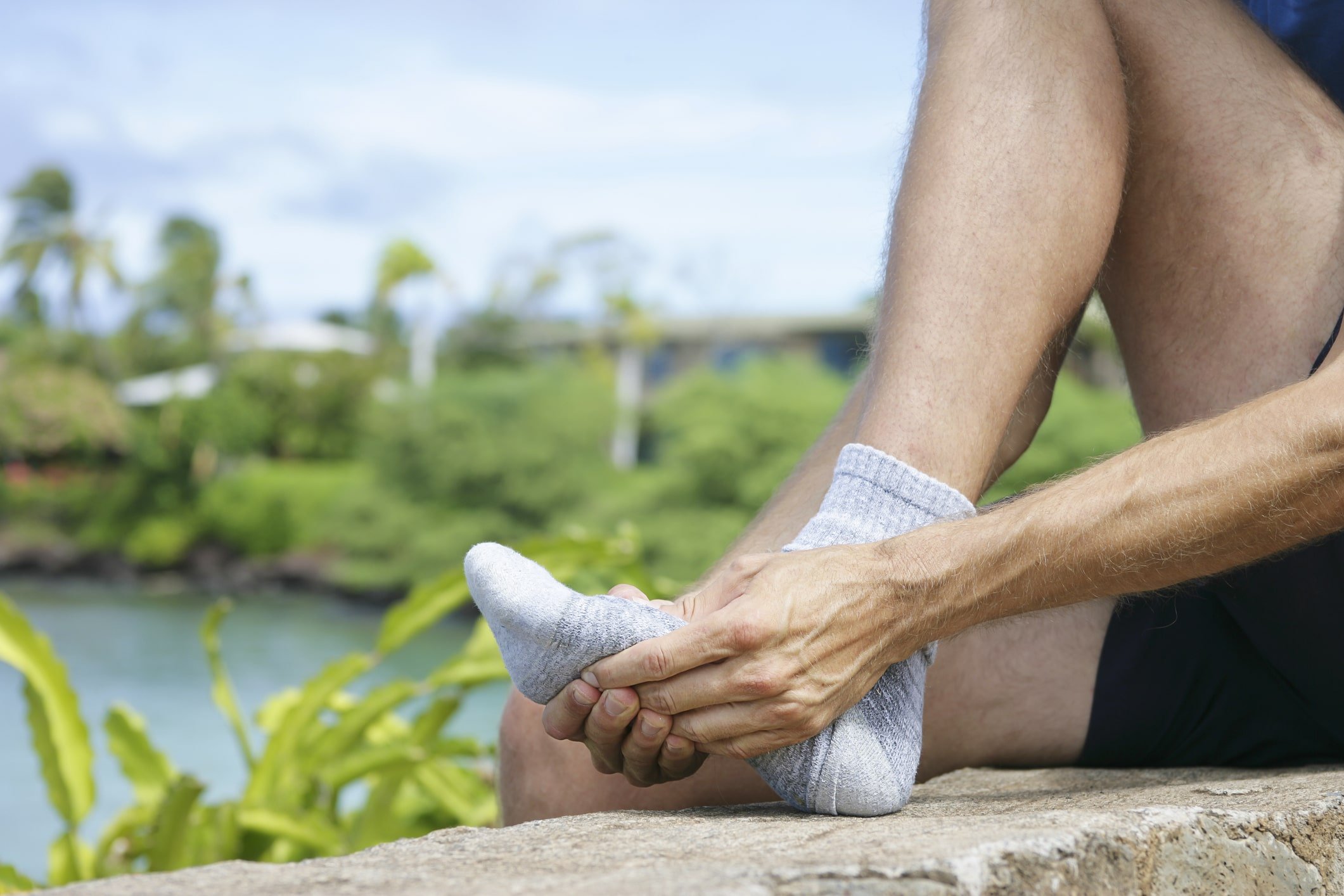


 Foot pain is something many people, especially athletes and active individuals, often deal with more frequently than they’d like to admit. It’s easy to dismiss as “just soreness” or assume it’s a natural part of aging. But here’s the thing: foot pain is usually your body’s way of waving a red flag. It’s not just an inconvenience; it’s a sign that something’s off in the way your body is moving - it's a warning sign. It is rarely “just soreness” or “part of getting older.” Instead, it’s often the result of underlying biomechanical issues that deserve attention and early intervention.
Foot pain is something many people, especially athletes and active individuals, often deal with more frequently than they’d like to admit. It’s easy to dismiss as “just soreness” or assume it’s a natural part of aging. But here’s the thing: foot pain is usually your body’s way of waving a red flag. It’s not just an inconvenience; it’s a sign that something’s off in the way your body is moving - it's a warning sign. It is rarely “just soreness” or “part of getting older.” Instead, it’s often the result of underlying biomechanical issues that deserve attention and early intervention.


